Imagine waking up one day and realizing you cannot work due to a debilitating health condition. Millions of people face this situation every year, making long term disability insurance a crucial safety net. This type of insurance ensures financial stability by replacing a portion of your income during extended periods of inability to work.
In this guide, we will cover:
- What long-term disability insurance is
- Differences between short term disability vs long term disability
- Common medical conditions that qualify
- How to apply for benefits
- Tips for increasing approval chances
By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of how Long Term Disability Insurance works, how much it costs, and how to protect yourself financially.
Understanding Long Term Disability Insurance
Long term disability insurance (LTD) is designed to protect your income when you are unable to work for an extended period due to illness or injury. While short term disability insurance covers temporary issues like minor surgeries or maternity leave, long-term disability insurance kicks in when the illness or injury prevents you from working for months or years.
Typically, LTD policies cover 50-70% of your salary and are offered as group plans through employers or as individual policies purchased independently.
What Is Long Term Disability?
At its core, long-term disability is coverage for the loss of ability to work over an extended period due to medical conditions. Policies often define disability as the inability to perform your “own occupation” or any occupation for which you are reasonably qualified.
According to the Council for Disability Awareness, musculoskeletal disorders are the most common claim, accounting for 29% of all long-term disability cases. Other major categories include mental health disorders, autoimmune diseases, and chronic illnesses.
Why it matters: Long term disability insurance provides financial stability, helping you pay for essentials like mortgage, groceries, and medical bills when you cannot earn a living.
Difference Between Short-Term and Long-Term Disability
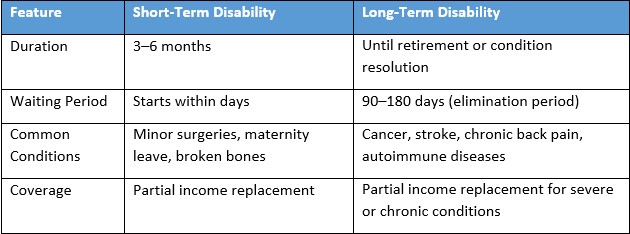
Example: A broken leg may qualify for short term disability, while chronic back pain or multiple sclerosis would fall under long term disability.
How Long Does Long-Term Disability Last?
The duration of LTD benefits depends on the policy and medical condition:
- Many policies last until retirement age
- Some cap at 2-5 years for specific conditions
- Mental health claims are often limited to 24 months
- Conditions like multiple sclerosis may qualify for lifelong benefits if the disability persists
- Factors such as age, severity, and occupation also influence the benefit period.
What Medical Conditions Qualify for Long-Term Disability Benefits
SSA’s List of Qualifying Impairments
The Social Security Administration (SSA) maintains a Blue Book of impairments severe enough to qualify for SSDI. Some categories include:
- Musculoskeletal Disorders: Chronic back pain, arthritis, fibromyalgia
- Special Senses & Speech: Blindness, deafness, diabetic retinopathy
- Respiratory Disorders: COPD, asthma, cystic fibrosis
- Cardiovascular: Heart failure, arrhythmias, coronary artery disease
- Digestive Disorders: Crohn’s disease, liver failure, IBD
- Genitourinary Disorders: Kidney failure requiring dialysis
- Hematological Disorders: Sickle cell disease, anemia
- Skin Disorders: Chronic dermatitis, severe burns
- Endocrine Disorders: Diabetes with complications like neuropathy
- Neurological Disorders: Multiple sclerosis, epilepsy, Parkinson’s
- Mental Disorders: Depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia
- Cancer: Leukemia, malignant tumors
- Immune Disorders: Lupus, HIV/AIDS, rheumatoid arthritis
To qualify, conditions must last at least 12 months and impair your ability to work.
To be eligible, your condition should meet listing criteria or be of equal severity and must last at least 12 months. SSA considers whether you are able to perform any work.
As an example, Stages of dementia and frontotemporal dementia belong to the neurological or mental category, which is a cognitive limitation. Mental disorders were found to be 9% of SSDI awards.
Common Conditions in Private LTD Claims
Private insurers often approve a broader range of conditions:
- Musculoskeletal Issues: Back injuries, carpal tunnel, degenerative disc disease (31% of claims)
- Cancer: Breast, lung, prostate
- Cardiovascular: Stroke, heart attack
- Nervous System Disorders: Migraines, neuropathy
- Mental Health: Anxiety, PTSD (10–15% of claims)
Other qualifying conditions include chronic fatigue syndrome, sleep apnea, ulcerative colitis, and fibromyalgia. Minor illnesses like colds or flu are not eligible.
Evidence Required for Approval
To maximize your chances of approval:
- Collect complete medical history and treatment records
- Document work limitations with functional assessments
- Include expert opinions from physicians
- For mental health, provide psychiatric evaluations and therapy records
Mental Health Conditions That Qualify for Long-Term Disability
Mental health disorders can significantly impair work capacity:
- Depression affects 21 million U.S. adults annually (NIMH)
- Bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, anxiety, PTSD qualify when symptoms prevent substantial work
- Dementia and frontotemporal dementia may qualify under neurological listings
- Severe autism spectrum disorders in adults can be eligible
Tips for Claiming Mental Health Disability:
- Document daily symptoms
- Track work impact (missed days, productivity issues)
- Obtain multiple expert opinions
Challenges: Stigma and subjective symptoms can complicate approvals. Continuous therapy proof and detailed documentation often aid successful claims.
Challenges in Mental Health Claims
Stigma and subjective symptoms complicate approvals. Insurers may require ongoing therapy proof. Appeals often succeed with detailed journals and witness statements.
Chronic Illnesses and Autoimmune Disorders
Chronic and autoimmune conditions often qualify:
- Lupus causes fatigue and pain
- Rheumatoid arthritis restricts mobility
- Diabetes complications like neuropathy or kidney disease
- Crohn’s disease exacerbations
Managing Chronic Conditions for Benefits:
- Follow treatment plans strictly
- Use wearable trackers to collect symptom data
- Join support groups for additional documentation
Fluctuating symptoms may extend disability periods. Integrative therapies, such as dietary changes, can support claims.
Long Term Disability Insurance Cost
Disability insurance price varies based on:
- Age and health status
- Occupation and risk level
- Benefit amount and waiting period
- Group vs individual plan
Example: Individual long term disability insurance cost can range from $50–$500 per month depending on coverage. Employer-provided plans are often cheaper or subsidized.
How to Apply for Long-Term Disability Benefits
SSDI Application
- Visit SSA.gov or call 1-800-772-1213
- Submit medical records and work history
- Be prepared for potential denials (≈60% of first claims) and appeals
Private LTD Application
- Contact your insurer after the elimination period
- Submit diagnosis, treatment records, and functional assessments
- Track expenses related to the condition
Tips for Successful Applications:
- Gather medical documents early
- Consult a long-term disability lawyer if necessary
- Explain how the condition affects job duties
- Maintain organized timelines and documentation
Common Mistakes to Avoid:
- Incomplete forms
- Misrepresenting severity
- Missing updated medical tests or employer statements
When to Consult a Long-Term Disability Lawyer
A lawyer can help navigate:
- ERISA laws for group plans
- Appeals after denials
- Collecting supporting evidence
- Negotiating settlements
Benefits of Hiring a Lawyer:
- Increase approval rates by up to 50%
- Expert handling of paperwork and deadlines
- Contingency-based fees for affordability
Choosing the Right Lawyer:
- Board-certified specialists
- Positive client reviews and high success rates in similar claims
Conclusion
When considering what medical conditions qualify for Long term disability insurance, a wide range of possibilities comes to mind, including musculoskeletal disorders and neuropsychological conditions such as dementia and frontotemporal dementia. The listings offered by SSA offer a structure and the common claims such as cancer and arthritis are covered under private insurance.
This knowledge will make you gain what you rightfully deserve to ensure that you are financially healthy even in times of adversity. Remember, early action prevents hardships. Today, consult a long-term disability attorney or visit SSA. To find out more about short term disability vs long-term disability or even how to get insured, refer to our related posts. Control your future today.
Key takeaways:
- Musculoskeletal, neurological, and chronic conditions are common claims
- Mental health disorders, autoimmune diseases, and cancer may qualify
- Proper documentation, professional advice, and organized applications boost approval chances
By taking action early, you can protect your income, pay bills, and ensure stability. Consult a lawyer, review your policy, and explore LTD insurance options today. For related insights on short term and Long term disability insurance.











