To understand your health, you should first learn your Body Mass Index (BMI). BMI is an easy calculator that approximates whether you carry a healthy weight given your height. This free BMI calculator will help you determine in seconds whether you are underweight, at the normal body weight, overweight, or obese.
BMI is not a number, and it is a significant measure of health that is often considered by doctors, nutritionists, and fitness experts to determine risks to weight. Whether you are going on a diet, embarking on an exercise regimen or simply keeping tabs on your health, you can easily keep track of progress with this BMI calculator.
What is BMI?
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a numerical value calculated using a person’s weight and height. It is widely used to categorize individuals into different weight ranges, which can indicate potential health risks.
- Formula (Metric): BMI = weight (kg) ÷ [height (m)]²
- Formula (Imperial): BMI = (weight (lbs) ÷ [height (in)]²) × 703
Why is BMI Important?
- Give a brief report on your weight status.
- Help in assessing risk of heart disease, diabetes and other health disorders.
- Useful to create weight loss or fitness goals.
Nevertheless, BMI is not an ideal measurement. It does not measure body fat directly or count muscle mass, but it is a useful screening measure of general health.
How to Use the BMI Calculator
Using our BMI calculator is simple and takes only a few seconds.
Step-by-Step Guide
- Choose your unit system – Select between Metric (kg, cm) or Imperial (lbs, ft/in).
- Enter your weight – Add your body weight in the appropriate unit.
- Enter your height – Provide your height in centimeters (metric) or feet and inches (imperial).
- Optional details – Add age and gender for more personalized results.
- View results instantly – Your BMI, category, and health tips appear automatically.
This tool works in real time, so as you adjust your weight and height values, the BMI updates immediately.
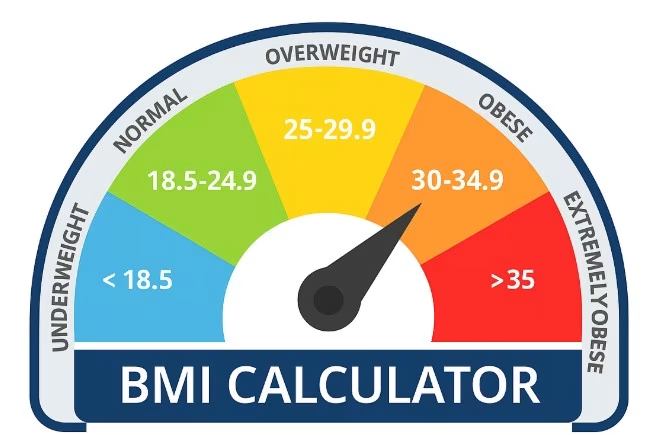
BMI Categories and Their Meanings
Your BMI result will fall into one of four main categories. Here’s what they mean:
Underweight (BMI < 18.5)
Being underweight may indicate that your body is not getting enough nutrition. Risks include weakened immunity, fatigue, and nutrient deficiencies.
Causes:
- Poor diet or low-calorie intake
- High metabolism
- Medical conditions (e.g., thyroid disorders)
Health Tips:
- Elevate calorie consumption with rich-nutrient foods
- include healthy fats (avocados, nuts, olive oil)
- Resistance exercise to fight body fat and build muscle mass
- Visit Doctor if there are underlying health issue
Normal Weight (BMI 18.5 – 24.9)
This range is considered healthy. People with normal BMI have a lower risk of weight-related diseases.
Benefits of being in this range:
- Better heart health
- Lower risk of diabetes
- Improved mobility and energy levels
Health Tips:
- Maintain a balanced diet with proteins, carbs, and healthy fats
- Exercise at least 150 minutes per week
- Stay hydrated and get 7–8 hours of sleep daily
Overweight (BMI 25 – 29.9)
Being overweight means, you carry more weight than what is considered healthy for your height.
Health Risks:
- Increased risk of high blood pressure
- Type 2 diabetes
- Joint pain and mobility issues
Health Tips:
- Reduce portion sizes and avoid processed foods
- Engage in regular cardio exercises (walking, cycling, swimming)
- Include strength training 2–3 times a week
- Gradually reduce calorie intake
Obese (BMI 30 and above)
Obesity significantly raises the risk of chronic illnesses and should not be ignored.
Health Risks:
- Heart disease and stroke
- Sleep apnea and breathing problems
- Certain cancers
- Fatty liver disease
Health Tips:
- Work with a nutritionist or healthcare provider
- Start with small lifestyle changes
- Avoid crash diets—focus on long-term sustainability
- Combine diet, exercise, and medical guidance if necessary
Health Tips Based on BMI Results
Depending on your BMI range, here are some general guidelines:
- Underweight: Eat more calorie-rich, healthy meals, and strength-train.
- Normal weight: Keep up your current lifestyle with balanced nutrition and exercise.
- Overweight: Focus on portion control, increase physical activity, and track progress.
- Obese: Seek professional medical guidance, start with light exercise, and prioritize long-term health.
These tips are general and may not apply to everyone. Always consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Limitations of BMI
While BMI is widely used, it has limitations:
- Doesn’t measure body fat: A muscular person may have a high BMI but low body fat.
- Not accurate for children or elderly: Growth stages and aging affect BMI reliability.
- Doesn’t account for gender or ethnicity: Different populations may have different healthy ranges.
Alternatives to BMI
- Body Fat Percentage – measured via calipers or bioelectrical impedance.
- Waist-to-Hip Ratio – indicates fat distribution.
- Waist-to-Height Ratio – another simple health metric.
Why Track Your BMI?
Tracking BMI regularly can help you:
- Identify potential health issues early.
- Adjust diet and exercise habits proactively.
- Stay motivated by monitoring progress.
- Set realistic weight and fitness goals.
BMI should be one of many health indicators, alongside blood pressure, cholesterol, and lifestyle factors.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the normal BMI range?
A BMI between 18.5 and 24.9 is considered normal for adults.
How can I lower my BMI?
- Eat a calorie-controlled diet.
- Exercise regularly (cardio + strength training).
- Stay consistent with small lifestyle changes.
What BMI is considered obese?
A BMI of 30 or higher is categorized as obese.
Can BMI be different for men and women?
The BMI formula is the same, but body composition differs by gender, which may affect interpretation.
Is BMI accurate for athletes?
Not always. Athletes may have higher BMI due to muscle mass, even if they have low body fat.
Does BMI change with age?
Yes, BMI interpretation can vary with age, especially for children and seniors.
Can children use BMI calculators?
Children’s BMI is measured differently, using growth charts instead of fixed ranges.
How often should I check my BMI?
Checking once every few months is enough unless you are actively trying to lose or gain weight.
What’s the difference between BMI and body fat percentage?
BMI uses weight and height, while body fat percentage directly measures fat tissue in the body.
Conclusion
BMI is an easy but useful indicator of your health condition. This BMI calculator can instantly inform you of your standing and can help you to stay healthy or healthy or, alternatively, advise you on how you can improve your health.
Takeaway: BMI is just a starting place. To obtain personal advice, one should always consult a healthcare provider. Use this calculator regularly, combine with healthy lifestyles and manage your health today.










