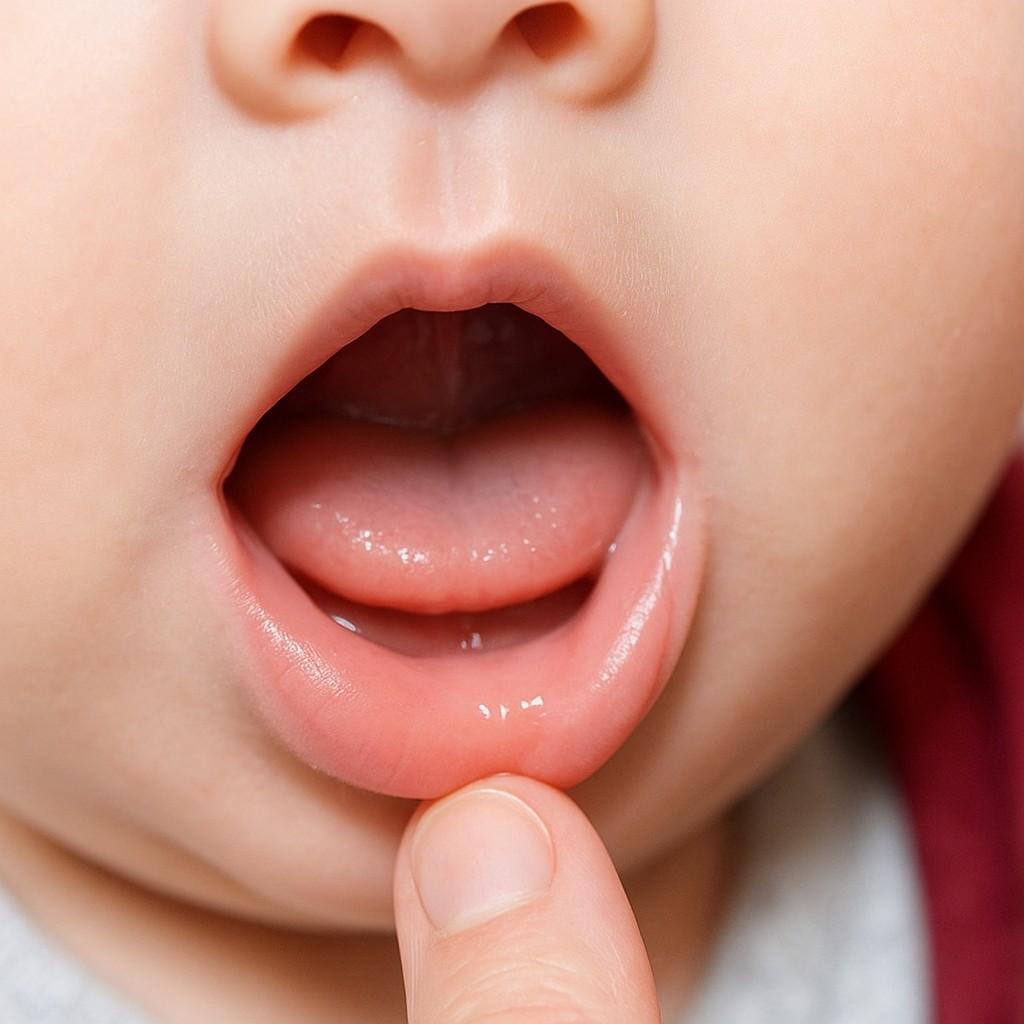
Is your baby struggling to latch during breastfeeding or showing signs of feeding discomfort? It could be more than just a phase — a condition known as lip tie might be the cause.
Understanding the symptoms and treatment of lip tie is essential for ensuring your baby’s healthy growth and development.
What Is a Lip Tie?
A lip tie occurs when the maxillary labial frenulum, the band of tissue connecting the upper lip to the gums, is unusually short, thick, or tight.
This anatomical variation can restrict the upper lip’s movement, potentially affecting oral function and, in some cases, breastfeeding efficiency.
Unlike tongue tie, the clinical significance of lip tie is less understood and remains a subject of ongoing debate among medical professionals.
How Common Are Lip Ties?
Lip ties, though often found with tongue ties, are less common and have a less direct link to feeding difficulties.
While tongue ties can cause latching problems, a lip tie may only slightly affect breastfeeding by limiting the lip’s movement.
The connection between lip ties and feeding issues is not as clear, with many babies feeding well despite the condition. However,
in some cases, a lip tie may contribute to nipple pain or inefficient milk transfer.
Understanding the Condition and Its Impact

“Lip tie occurs when the upper lip is anchored too tightly to the gum, limiting natural movement and sometimes affecting feeding.”
— Dr. Sarah Collins, Pediatric ENT, 2025
Lip tie, medically known as a labial frenulum restriction, is a condition in which the tissue (frenulum) connecting the
upper lip to the gums is unusually short, thick, or tight. This can make it difficult for babies to flange their lips outward—an
essential motion for effective breastfeeding.
Common signs include:
-
Difficulty latching or staying latched during feeds
-
Excessive gas or fussiness during feeding
-
Poor weight gain despite frequent nursing
-
Soreness or pain in the mother’s nipples
In toddlers, a severe lip tie may also contribute to:
-
Speech development issues
-
Gap between upper front teeth
-
Challenges in maintaining oral hygiene
However, not all lip ties cause problems. Some are mild and do not interfere with feeding, speaking, or dental health.
A professional evaluation by a pediatrician, lactation consultant, or pediatric dentist can help determine whether treatment is necessary or if monitoring is sufficient.
Symptoms and Signs in Babies
| Feeding Difficulties
Babies may struggle with latching onto the breast or bottle or have trouble maintaining a seal during feeding. |
Inefficient Feeding
Signs include fatigue or fussiness during feeds, leading to prolonged feeding times, or slow/poor weight gain due to inadequate milk transfer. |
| Maternal Discomfort
Mothers might experience nipple pain, engorgement, or recurrent blocked milk ducts as a result of the baby’s ineffective latch. |
Auditory & Respiratory Cues
Some infants may produce clicking sounds while feeding, or exhibit subtle breathing difficulties, indicative of an compromised oral seal. |
Controversies and Expert Opinions
“Many experts believe lip ties rarely cause significant breastfeeding problems and often improve naturally as children grow.”
4 BabyCenter 2025
Leading organizations like the American Academy of Pediatrics typically do not recommend routine lip tie surgery for isolated breastfeeding issues.
A multidisciplinary feeding evaluation involving lactation consultants and pediatricians can often provide effective non-surgical solutions.
Diagnosis Challenges
Lack of Standardization: There is no universally accepted measurement or classification system to reliably define when a frenulum is problematic.
Inconsistent Assessments: Studies indicate poor agreement among clinicians when assessing lip tie severity, with existing tools like the Kotlow classification showing low reliability.
Focus on Function: Diagnosis should prioritize the functional impact on feeding and oral development, rather than solely relying on the visual appearance of the frenulum.
This diagnostic variability underscores the importance of a comprehensive approach to assessment, integrating observations of feeding mechanics and symptom history.
Treatment Options
Conservative Management
- Working with a certified lactation consultant to optimize latch and feeding positions.
- Implementing targeted oral exercises to improve lip mobility.
- Addressing maternal factors that may influence breastfeeding success.
Frenotomy (Surgical Release)
- A quick procedure to release the frenulum, often performed with scissors or laser.
- Generally considered controversial for lip tie, often reserved for severe cases where functional impairment is clearly confirmed and other interventions have failed.
- Research suggests that many babies referred for surgical intervention do not ultimately need it after a thorough, multidisciplinary evaluation.
The decision for intervention should always be made after careful consideration and comprehensive assessment by qualified healthcare professionals.
Lip Tie Awareness and Treatment Outcomes
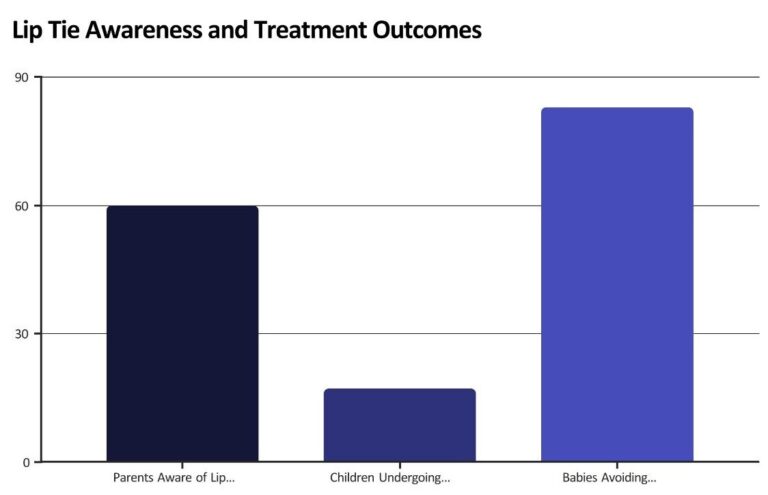
This chart highlights the significant awareness of lip ties among parents and the number of children undergoing surgery, contrasting with the high percentage of babies who avoid surgery after a comprehensive evaluation. The increase in tongue-tie surgeries also underscores a broader trend in frenum procedures.
Real-World Impact: Parent and Clinician Perspectives
Parents are increasingly exposed to information about lip ties through social media (68.4%), often before consulting medical professionals. This strong reliance on non-medical sources can heighten concerns and prompt questions about surgical interventions, highlighting the critical need for balanced and accurate information dissemination.
87% of surveyed parents use social media daily, underscoring its influence.
Clinicians emphasize that a careful, functional assessment is crucial to
prevent unnecessary procedures. They advocate for supporting
breastfeeding success through evidence-based practices.
Conclusion: Navigating Lip Tie with Knowledge and Care
Common & Often Benign
Lip ties are prevalent but frequently do not cause significant issues and can resolve naturally.
Functional Assessment is Key
Prioritize a thorough functional assessment and multidisciplinary feeding support before considering surgery.
Seek Expert Guidance
Parents should consult pediatricians and lactation consultants, avoiding sole reliance on informal sources.
Empower with Education
Accurate education can reduce unnecessary interventions and improve infant feeding outcomes.